
How to Protect Your Privacy on Social Media
This page has been peer-reviewed, fact-checked, and edited by qualified attorneys to ensure substantive accuracy and coverage.
Social media privacy is almost an oxymoron. Social media, by its very nature, is public. It connects people across the globe and provides a convenient forum for sharing information with others. But some information is best kept private.
If you like socializing on social media, but do not want to expose yourself to malicious internet actors and predators there are things you can do to enhance your privacy. Here are eleven ways you can take control over your social media privacy:
- Read the platform’s Terms of Service;
- Review the platform’s Privacy Policy and adjust your privacy settings;
- Only accept friend requests from people you know;
- Be careful what you post;
- Remove personal identifying information;
- Turn off location features;
- Choose a strong and unique password;
- Turn off “check-in” and location features;
- Be careful when using public wireless connections;
- Know who can see your information without your consent; and
- Know the types of information you should avoid sharing.
At Minc Law, we make it a priority to help individuals and businesses protect their online assets. That is why we offer services to help clients monitor and protect their online reputation – from digital risk protection to combating sextortion.
Video: How to Protect Your Privacy on Social Media

In this guide, we will explain why it is so important to protect your privacy on social media and the type of information social platforms share. We will conclude with ways to protect your private information while still enjoying your favorite social media platforms.
Importance of Protecting Your Social Media Privacy
Social media provides an outlet for users to share things about their personal lives – from pictures to political ideologies and everything between. With billions of people using social media daily, you may have never thought about how many people are viewing your content.
While 61% of Americans say they would like to do more to protect their privacy, nearly half of all social media users admit they are unsure whether their data is secure. In a nutshell, social media users value their privacy but do not trust social media platforms to keep data private. And there is good reason for this lack of trust.
The Cambridge Analytica Data Scandal
In 2018, The New York Times dropped an incriminating report highlighting a data scandal between Facebook and Cambridge Analytica. The British consulting firm, Cambridge Analytica, acquired and used private personal data from Facebook users. According to Facebook, a researcher said they were collecting the data for academic purposes. However, allegations surfaced that the personal data was being used to influence the outcome of elections.
Whistleblowers who were once employed by Cambridge Analytica admitted that data from roughly 87 million Facebook users were used to create “psychographic” profiles of people so they could be targeted with persuasive political messages. Ultimately, Facebook was fined for the data harvesting scandal and Cambridge Analytica was forced to shutter its operation.
The Cambridge Analytica story made international news, but they are far from the only company using social media data. Whether you are aware of it or not, companies have been breaching user’s privacy on social media for years. Companies, researchers, marketing agencies, and the government have been known to collect information about individuals through social media.
This process is sometimes referred to as “social media mining” or data mining. By extracting and analyzing social media data, outside entities find patterns of user behavior – which they then use for whatever their goals may be. Marketing agencies might be looking for buyer behaviors so they can launch highly targeted and profitable advertising campaigns. The government, on the other hand, may mine social media data to surveillance criminal activity and national security threats.
Why is Social Media Privacy Important?
You may have heard others say, “I am not worried about what I post on social media, I have nothing to hide.” Perhaps you have even said it yourself. While this may be true, there is still good reason to value your online privacy.
There are inherent risks of sharing information and meeting new people online. The information shared on social media can influence your reputation, as well as your relationship and career prospects.
Employee Social Media Privacy
There are currently no federal laws that prohibit employers from monitoring their employees on social media. Unfortunately, most people have no way of knowing whether their job rejection, demotion, or termination are the result of content posted on social media.
In fact, nearly 8 out of 10 employers have rejected an applicant based on what they found on the applicant’s social media. Beyond that, more than 1/3rd of employers admitted to reprimanding or firing an employee based on that employee’s online content.
The statistics are grim, but the good news is that you can prevent issues with your current or future employers with some simple tasks. Setting your profile to private is one way to keep your social media from being used against you, but we will cover some more detailed steps in the sections that follow.
What Information Are You Sharing When You Use Social Networks?
You might be surprised to learn all the information you are actually sharing on social media. Personal information that you are sharing (knowingly or unknowingly) includes:
- Your full name,
- Photos of yourself and family members,
- Your birthdate,
- Where you went to school,
- Where you work now (and former employers),
- The city and state where you currently live as well as prior addresses,
- Your cell phone number and possibly your email address,
- Interests such as movies, music, and book that you like, and
- Religious, political, and social affiliations.
Sharing personal information like that listed above can open you up to scams, identity theft, hacking, online predators, sextortion, and other issues.
What Are the Consequences of Failing to Protect Your Social Media Privacy?
Many people fail to take steps to protect their social media privacy, and the consequences can be dire. Below are several serious privacy threats associated with social media.
Phishing Attempts
Phishing attempts are communications from cybercriminals that come in the form of an email, direct message, text, or phone call in an attempt to access your sensitive personal information.
Malware Sharing
Malware is software designed to gain access to your computer or device. Once malware software is installed, it can be used to steal personal information, including banking data.
Botnet Attacks
Like malware, bots are a type of software programmed to perform a specific, repetitive task. For instance, a social media bot might be programmed to follow or respond to users who mention a certain keyword.
A large group of bots is called a botnet. Both bots and botnets are heavily involved in social media and are used to steal data, send spam, and distribute DDoS attacks.
Data Mining
We briefly mentioned data mining when we discussed the Cambridge Analytica/Facebook data scandal. Essentially, data miners collect data stored on social media and then distribute it to companies who are trying to target advertising of their product or services to consumers.
Any information that you share with social media can be mined, but data that is popular among miners include your name, birthday, location, personal interests, and how you interact with the platform.
Sextortion
Sextortion is a serious crime that happens when a scammer threatens to release explicit images or videos of you unless you meet their demands to send them money (in most cases).
These types of scammers and criminals lurk on social media and prey upon people who are willing to accept friend requests and messages from random profiles. Once they gain your trust, they persuade you to send compromising images of yourself and then blackmail you in exchange for money or sexual favors.
For example, a common Facebook sextortion scam typically begins with the victim receiving a friend request from a complete (and charming) stranger. After some back and forth, the stranger then convinces the victim to share explicit or intimate photos, videos, or messages. The perpetrator then threatens to share or publish the images, videos, or text messages, unless a ransom is paid.

How to Control Your Privacy on Social Media
Social media is so intertwined with our daily lives that many people do not stop to think about their privacy while using these platforms. Most of us do not realize that social media privacy is not automatic, and we have to take steps to secure our own personal information. These include:
- Reading the Terms of Service,
- Reviewing the social media website and/or app’s privacy features,
- Only accepting friend requests from people you know,
- Thinking twice before posting,
- Keeping your personally identifiable information private,
- Turning off location data,
- Understanding the personal data that can be shared without your consent,
- Knowing the types of information you should avoid sharing online.
1. Read the Privacy Terms
Every social media website and app has Terms of Service (TOS) and privacy terms. We recommend reading and understanding the privacy terms before you make an account.
The Terms of Service will help you understand what information the social media site is sharing with third parties. It will also let you know if (and how) you can delete content or your account.
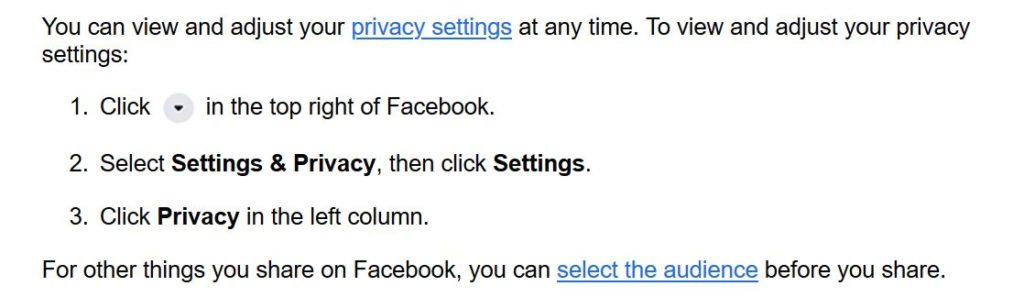
2. Review the Platform’s Privacy Features and Adjust Accordingly
Nearly every social media platform enables you to adjust privacy settings. Log into your profile and you can view your default privacy settings and adjust accordingly.
At Minc Law, we recommend ramping up your privacy settings as high as you can. For example, we suggest only allowing your Facebook posts and pictures to be visible to your friends.
3. Only Accept Friends or Follow Requests From People You Know
This is a big one! You do not have to accept every single friend or follow request, because some of those strange requests could be from cybercriminals.
Accepting friend requests from people that you do not know opens you up to scams, like sextortion. This is especially true for children. Talk to children and teenagers about refusing friend requests or follows from people that they do not know to avoid being the target of online predators trying to solicit minors.
4. Be Careful What You Post
Posting pictures seems like a normal thing to do on social media, but you might want to think twice before doing so. Posting pictures of children, especially, should be done with caution. Cybercriminals can use those photos to digitally kidnap your child’s identity – and identity theft is not rare.
Even the rich and famous are not immune to cyber-crimes. Well-known influencer, Kim Kardashian shared a photo on social media of a 4.5 million-dollar diamond ring purchased for her by then-husband Kanye West. Unfortunately, some of Kardashian’s social media followers had criminal intent.
Two men entered the hotel where Kardashian was staying during Paris Fashion Week and robbed her at gunpoint. They stole more than $9 million in jewelry and left Kardashian bound in handcuffs. A police investigation led to the arrest of 17 individuals, some of whom had been following Kardashian’s social media for years. While this is an extreme example, it can be dangerous to post flashy photos of cars, electronics, and jewelry that might appeal to criminals.
It is worth pointing out that public shaming on social media can also come with consequences. While online shaming has grown in popularity, it is a knee-jerk reaction that has led to many people getting fired.
Worse yet, spreading lies or harmful posts that you have not verified can lead to lawsuits over social media defamation. Social media may seem like a great place to call out the negative behavior of others – but it can come back to bite you, so it is best to think twice before you post anything negative about another person online.
Related Video: What to Do If You Are the Target of Social Media Defamation

5. Remove Personal Identifying Information
It is wise to keep your identifying information private, like your full name, birth date, and address. While you may need to provide this information to the platform to create an account, you should not share this information on your profile or within posts. It almost goes without saying that you should not post your social security number, credit card, or banking information.
Also, use caution when sharing information about your daily life – like what school your children attend and where you work. Sharing too much information makes you an easy target for internet criminals.
For Americans, the responsibility falls on us to protect our own personal information, but some other countries have taken steps to protect the privacy of their citizens. In the European Union, the General Data Protection Regulation contains a number of rules designed to protect how citizens’ online data can be used and shared.
Notably, E.U. citizens have “the right to be forgotten,” enabling them to have digital personal data erased if the information meets certain standards. To learn more about this rule, check out our article, “What is the Right to be Forgotten?”.
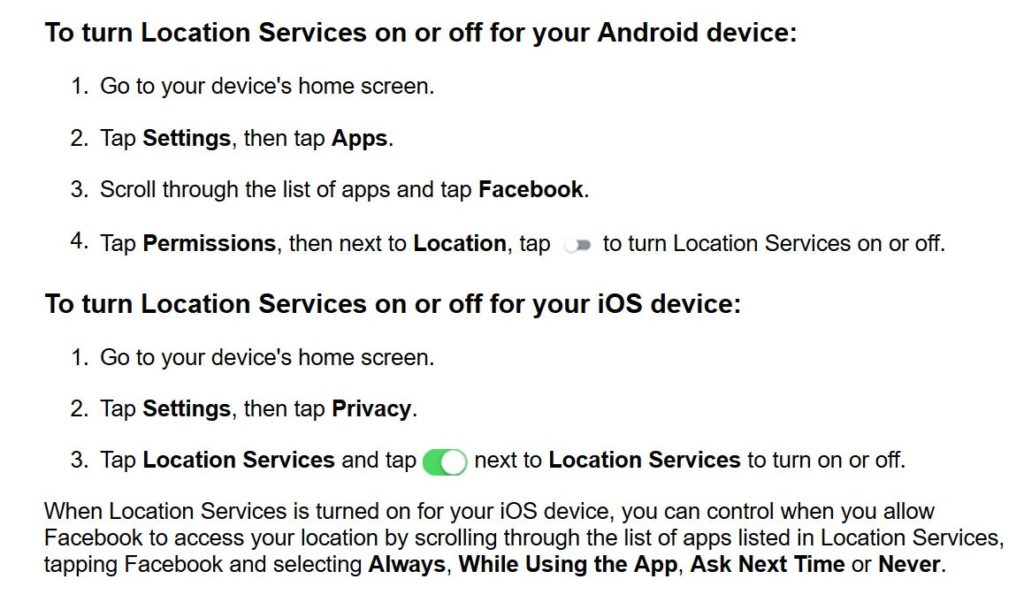
6. Turn off Your Location
Location data and social media check-ins broadcast to the world exactly where you are at any given time. This can be dangerous if you are dealing with a stalker – but the threat goes well beyond stalkers. Sharing posts that show you are on vacation advertises the fact that your house is empty, giving criminals the opportunity to target your home.
If you have children, you could be putting them at risk of unwanted contact or attention from strangers by sharing their location on social media. Your location data may also alert strangers that your children are home alone while you are out.
7. Know Who Can See Your Private Information on Social Media Without Your Consent
When you check a social media platform’s Terms of Service, pay close attention to who can see your private information without your consent. If you have not adjusted your privacy settings, anyone can see your profile and posts. However, even if you have implemented some privacy measures, the following third parties may still have access to your information:
- Advertising companies,
- Third-party applications,
- Government and law enforcement,
- Potential and current employers.
8. Know the Types of Information You Should Avoid Posting on Social Media
Not everything should be posted on the Internet. While loved ones may be interested in knowing exactly what is going on in your life, others may not have such benign motives. I will break this information into two categories: data you should absolutely avoid posting and data you should be cautious about posting.
Below, we begin with a look at the information you should not post under any circumstances.
Personal Information You Should Avoid Posting
Some information should not ever be shared online because it can be readily accessed and used by criminals. Even if you think your profile is completely private, others may see it on a mutual friend’s computer or device. Plus, information can always be screenshotted and shared without your consent.
Examples of information you should never share on social media are:
- Your address,
- Your phone number,
- Social security numbers,
- Full birthdates (including year of birth),
- Banking information,
- Your current location, and
- Vacation plans
Personal Information You Should Be Cautious of Posting
There are other types of information you should be especially cautious about posting because they can also be used for illegitimate purposes, even if you think your social media account is private.
You should think twice and exercise caution before posting:
- Vacation photos (while on vacation). This could alert others that your home is empty.
- Photos of your children. Child predators continuously find new ways to use the internet to prey on children and social media provides ample opportunity to groom unsuspecting minors. Armed with other social media information, predators may be able to ascertain where your children live, where they go to school, who their friends are, and other ways to gain your child’s trust.
- Employment information. If you list your current employment information, you open the door for your manager or boss to follow you on social media. For better or worse, anything you post online could reflect on your workplace – so it is wise to keep employment information off your social media accounts if you intend to use them for personal reasons. It is also not a good idea to complain about your job on social media, because more often than not, employers find out.
- Embarrassing photos. Most of us do not like to share photos where we are not looking our best. Yet, millions of embarrassing photos end up on social media. Perhaps you thought you looked cute in the photo where you were chugging shots in college, but your future employers may not have the same opinion. Photos that do not reflect the reputation that you wish to convey can hurt your chances of getting hired and even get you fired. You might want to adjust privacy settings so that you must approve any tagged photos before they are posted, to prevent friends from posting less-than-flattering images of you.
Online Reputation Tip: We do not always like the content we find about ourselves online. Fortunately, there are ways to overcome negative online content. Some content can (and should) be removed by legal means, like fake reviews and images posted to gossip forums. Other content can be suppressed through online reputation management (ORM). In fact, ORM might be your best option if you are dealing with newsworthy or viral content or content you need suppressed quickly.
Know What Types of Personal Data Social Media Sites Store & Share
Whether you know it or not, your personal data is being stored and shared by social media platforms. And it is all perfectly legal. While every platform is slightly different, the standard practice for most sites is to keep data encrypted while it is stored on their servers.
Anyone that wants access to the encrypted information will need a decoding key to unlock the information. At least, that is how data encryption is designed to work.
Data breaches happen and have grown quite common. In 2020 alone, 155.8 million individuals were affected by data exposure. As mentioned earlier, even large corporations like Facebook are not immune to data breaches. Savvy cybercriminals find ways to access some of the most secure data on the planet, so your best way to avoid data exposure is by limiting the information you share on social media.
Types of Data Social Media Sites are Collecting and Storing
Aside from what you post or voluntarily share on your profile, social media platforms collect much more detailed information.
Below are common types of personal data that social media platforms collect and store:
- Personal info used to create your account (name, birthday, phone number, email),
- Content you post or share (photos, location, videos, links),
- Interactions on the platform (who are you talking to and the content you engage with),
- Phone and social media contacts (if your phone is synced),
- Device information (operating system and IP addresses),
- Payment information and transaction activity (Purchases through the app, like games and Facebook’s marketplace activity).
You may not realize how much data you produce on social media, but it is highly valuable and can be used in sinister ways if it lands in the wrong hands.
Who Are They Sharing This Data With?
We mentioned earlier that social media platforms often share data with advertisers and government officials, but that is just the tip of the iceberg. Social platforms also share data with data mining companies (data brokers), vendors, and other social media networks.
For instance, Facebook and Instagram have common ownership and often share information with one another (even if you are not on both platforms). Data is also shared with researchers and academics (although Cambridge Analytica famously accessed Facebook data under the mere guise of research).
For more information on who your personal data is being shared with, check out each platform’s privacy policies.
How Your Personal Data May Be Used By Social Media Platforms & Third Parties
In some cases, data sharing is a necessity because social platforms need certain information to operate their service.
Some common reasons social media sites need your data is:
- To create your account,
- To send you promotional materials (email and newsletters),
- To send you administrative communications, like security alerts and policy updates,
- To provide user support,
- To track and measure website or app performance,
- To protect against and track illegal activity,
- To help prepare marketing ads and strategy, and
- To improve your overall experience with the platform.
Why Do Social Media Sites Share Personal Data With Third Parties?
One of the main reasons social media platforms collect and share data with third parties is to help companies understand what users are interested in and how they behave online. It can also help provide real-time demographic information.
How you use social media provides platforms with a lot of data about what is working and what is not, and they sell that data to other individuals. In fact, this is how platforms like Facebook, Twitter, Instagram, and TikTok make money. Their service is free to users, but others pay them to access the data gathered by their platform.
In a sense, third-party access to your personal data is (currently) the “price” you pay to use a particular platform.
Security Tips for Privacy on Social Media
Now that you know the type of information social media platforms are collecting, you might be wondering how you can maximize your privacy while still taking advantage of social media.
Here are 10 ways to secure your privacy on social media:
Choose a Strong and Unique Password
Having a strong and unique password can prevent you from having your accounts hacked and personal information stolen. In the following sections, I will explain how to establish a strong password that helps protect your information.
Do Not Use The Same Password For Everything
Using a single password makes it easy for hackers and cybercriminals to gain access to all your accounts.
Avoid Logging In to Social Media On Friends’ Devices or Public Devices
If you choose to access social media on a public device, be sure to log out. If you do not, the next person who uses that device will have access to your social media account and personal information.
Use Two-Factor Authentication for Accounts
Using two-factor authentication on your accounts will add extra security. If someone else tries to log in to your account, the platform will send a code to your phone or email address that you will need to enter before you can access the account.
Two popular authenticators that are worth checking out are Google Authenticator and Authy.
Turn Off “Check-in” And Location Features
Turning off your location is an important tip to avoid break-ins, robberies, or stalking crimes.
Avoid Sharing Too Much Personal Information
Hackers and other cyber attackers use whatever information they can gather from your social media profile (date of birth, education, pet’s name, etc.) to get into your accounts and possibly steal your identity.
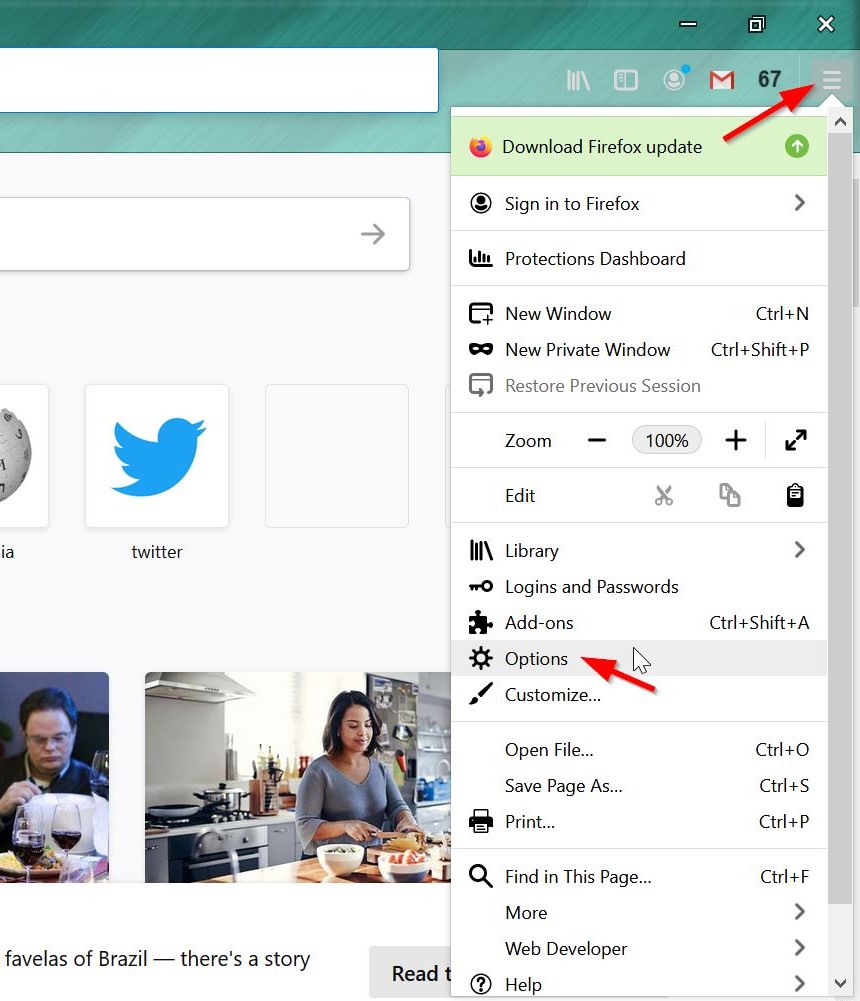
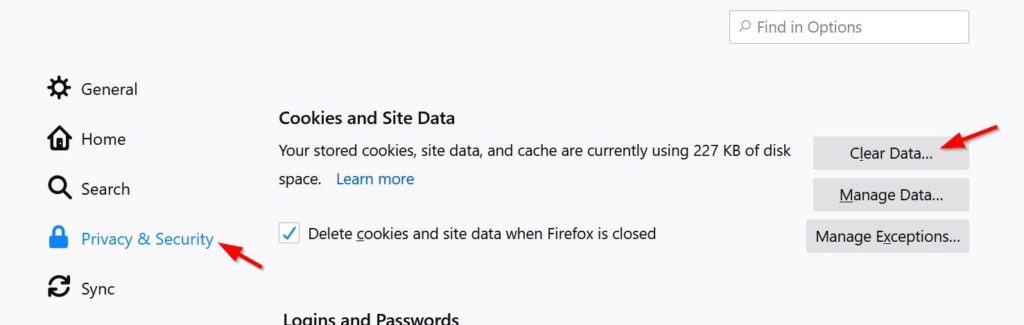
Delete Your Cookies Often
Deleting your cookies can help you reclaim a little bit of your privacy. Websites use cookies to track how many times you visit a site and to make a digital profile of your online activities.
By deleting cookies, you can prevent others from accessing your search history if you share a computer or device. It will also provide more privacy from website hosts and social media platforms who want to track you or serve targeted ads based on your viewing history.
Be Careful When Using Public Wireless Connections
Using a public Wi-Fi connection makes you vulnerable to having your passwords and usernames stolen.
Hackers can gain access to your computer and your personal information while you are connected to public Wi-Fi. To keep your information secure, use a private connection or VPN.
Use the Block Button
When you are sent sketchy links from unknown friends or spammers, we recommend ignoring them and blocking the user.
Likewise, if you receive a questionable link from a friend or family member, it could be the result of their account being hacked. It is better to be safe than sorry.
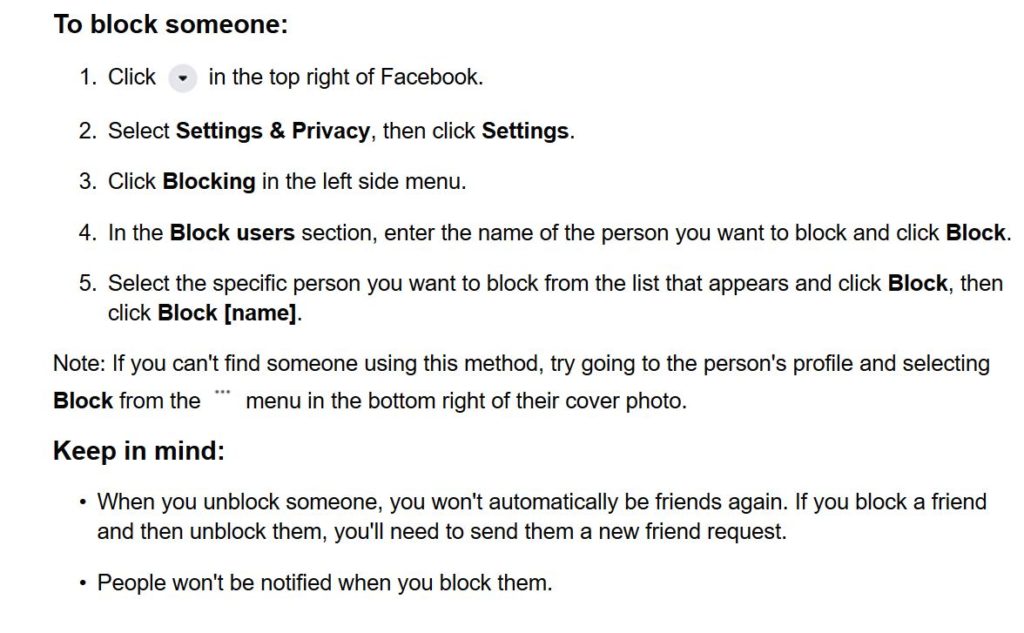
To block someone on Facebook, follow these steps:
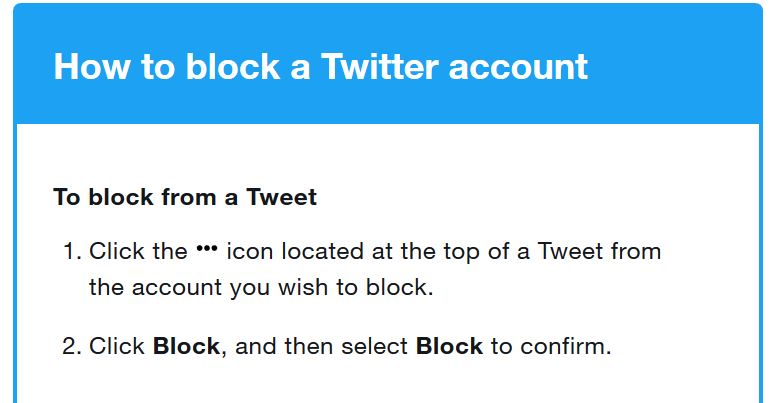
To block someone on Twitter, follow these steps:
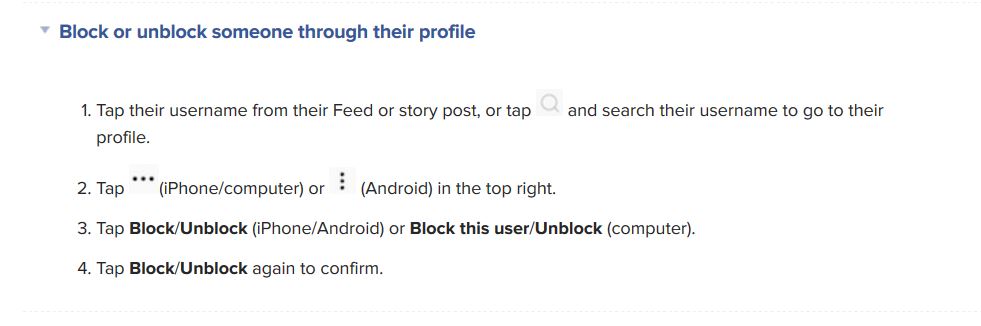
To block someone on Instagram, follow these steps:
How Important is a Strong Social Media Password?
One of the most important ways to protect your personal information is with a strong password. Most social media apps and websites encourage users to create strong and unique passwords by requiring a password with certain elements, often a combination of letters, numbers, and characters.
Here are two reasons why you should have a strong social media password:
- Keeping your password strong and unique reduces your chance of a cyber-attack. If your password is leaked during a data breach, cybercriminals can take that leaked password and look into other accounts that are associated with you, such as a work-related or bank account. They can then try to log into these important accounts with the exposed password, compromising your security.
- Cyber experts can also use a technique called a “brute-force attack”. This is where criminals try to guess every password possible until they identify the correct one. This technique works best with weak passwords like “Password123” that are easy to guess.
Experts agree that a strong password consists of 10 characters and includes a combination of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols. To ensure your password is unique, use a different password for each account.
Work With Experienced Internet Attorneys to Protect Your Privacy on Social Media
If you are concerned about protecting your privacy online, we recommend checking out our articles about digital risk protection. In a nutshell, digital risk protection is a way of protecting your assets and reputation from online threats and mitigating problems if the worst occurs.
Video: What is Digital Risk Protection? Minc Law’s DRP Service Explained

★★★★★
“Melanie was absolutely fantastic. Six years ago, someone wrote something terrible about me online and it followed me wherever I went! Jobs, relationships, etc. I finally got in touch with Minc, and Melanie was so courteous, professional, and diligent about getting the post removed. Thank God for Minc Law because I’m getting married next year, and I finally feel comfortable using my full name on my wedding announcements! Thank you, Minc!!!”
HCP, Sept 28, 2020
If you are already battling a data breach, facing online extortion, or the target of malicious internet attacks, our experienced internet attorneys can help. We have helped over 2,500 clients overcome internet threats – from online defamation to harassment, our attorneys have your back.
To schedule a free, no-obligation consultation with an intake specialist, call us at (216) 373-7706 or fill out our online contact form.





